Urolithin A (3,8-Dihydroxyurolithin) and related products
• Urolithin A (3,8-Dihydroxyurolithin)
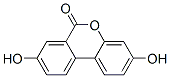
Product Name:3,8-dihydroxy-6H-dibenzo(b,d)pyran-6-one
CAS: 1143-70-0
Molecular Formula:C13H8O4
Molecular Weight:228.2
• Urolithin B (3-Hydroxyurolithin)
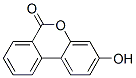
Product Name:3-HYDROXY-6H-DIBENZO[B,D]PYRAN-6-ONE
CAS: 1139-83-9
Molecular Formula:C13H8O3
Molecular Weight:212.2
• Urolithin D (3,4,8,9-Tetrahydroxyurolithin)
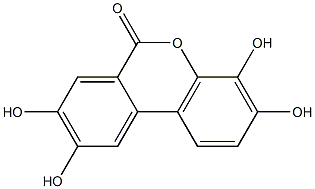
Product Name:Urolithin D
CAS: 131086-98-1
Molecular Formula:C13H8O6
Molecular Weight:260.19902
• Urolithin M-5
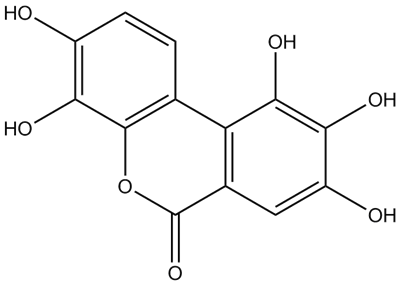
CAS Number: 91485-02-8
Molecular Formula: C13H8O7
Molecular Weight: 276.2 g.mol-1
• Urolithin M-6
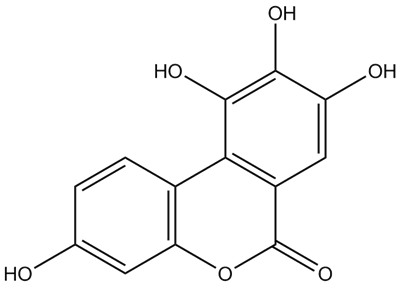
CAS Number: 1006683-97-1
Molecular Formula: C13H8O6
Molecular Weight: 260.2
• Urolithin M-7
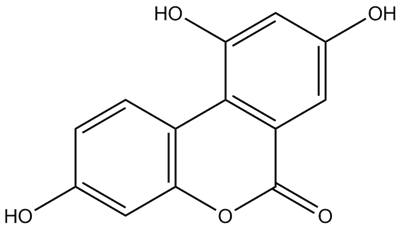
CAS Number: 531512-26-2
Molecular Formula: C13H8O5
Molecular Weight: 244.2
• Urolithin C (3,8,9-Trihydroxy urolithin)
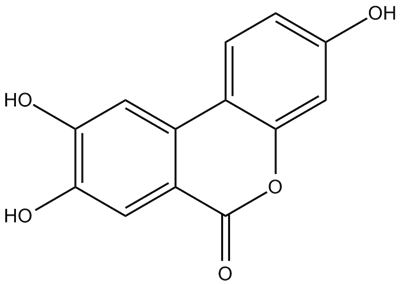
CAS Number: 165393-06-6
Molecular Formula: C13H8O5
Molecular Weight: 244.2
Urolithin A is not known to be found in any food. It forms as the result of transformation of ellagic acids and ellagitannins by the gut microflora in humans. Ellagic acid itself results from the hydrolysis of ellagitannins in the gut in the presence of water.
Sources of ellagitannins are: pomegranates, nuts, some berries (raspberries, strawberries, blackberries, cloudberries), tea, muscadine grapes, many tropical fruits, and oak-aged wines.
The conversion of the ellagic acids into urolithin A depends on individual microflora composition and can vary significantly.
Dietary source | Ellagic Acid |
Fruits (mg/100g fresh weight) | |
Blackberries | 150 |
Black raspberries | 90 |
Boysenberries | 70 |
Cloudberries | 315.1 |
Pomegranate | 269.9 |
Raspberries | 270 |
Rose hip | 109.6 |
Strawberries | 77.6 |
Strawberry jam | 24.5 |
Yellow raspberries | 1900 |
Nuts (mg/g) | |
Pecans | 33 |
Walnuts | 59 |
Beverages (mg/L) | |
Pomegranate juice | 811.1 |
Cognac | 31-55 |
Oak-aged red wine | 33 |
Whiskey | 1.2 |
Seeds (mg/g) | |
Black raspberries | 6.7 |
Red raspberries | 8.7 |
Boysenberries | 30 |
Mango | 1.2 |




